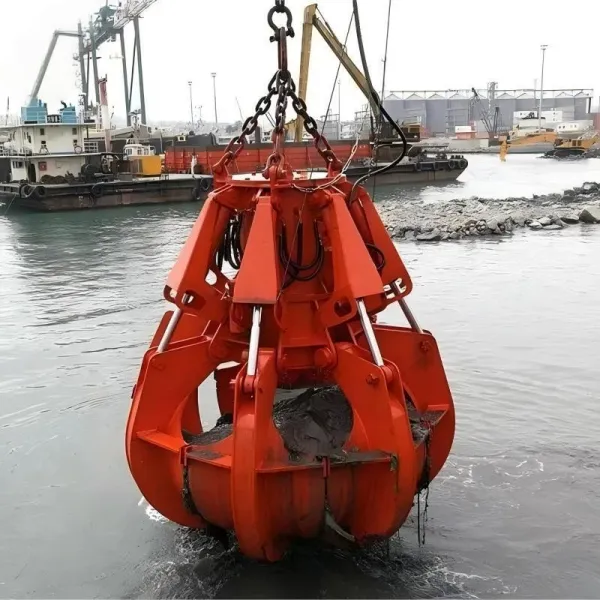
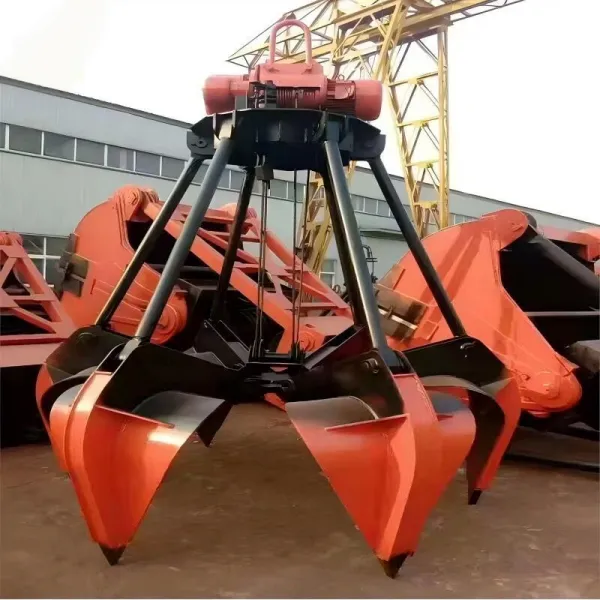
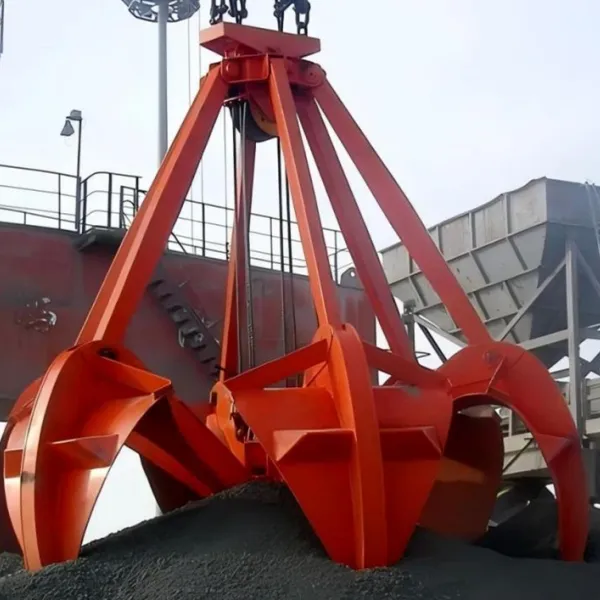
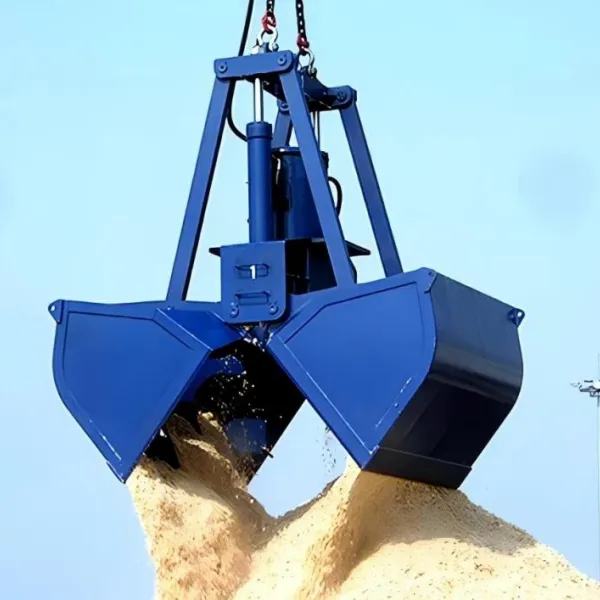
A Grab Bucket is a specialized device designed for grabbing, transporting, and unloading bulk materials. It is widely used in ports, mines, construction sites, and other scenarios to efficiently handle materials such as coal, ore, sand, scrap metal, and waste. Its core structure consists of two or more openable/closable jaws (or clamshells), driven by a power system to achieve material gripping and release.
Types of Grabs
Based on driving mechanisms, applications, and structural features, grabs are primarily categorized as follows:
By Driving Mechanism
1. Double-Rope Grab: Utilizes two steel ropes to separately control opening/closing and lifting. Simple in structure but requires a crane with dual winches.
2. Single-Rope Grab: Operates with a single steel rope for both opening/closing and lifting. Suitable for cranes with a single winch, though less efficient.
3. Electric-Powered Grab: Equipped with an internal motor, eliminating the need for external hydraulic or complex rope systems. Ideal for environments with stable power supply.
4. Hydraulic Grab: Driven by an external hydraulic system, offering high gripping force for heavy materials (e.g., ore, rock).
By Application and Structure
1. Multi-Jaw Grab (Clamshell Grab): Features multiple jaws for gripping irregular materials (e.g., scrap metal, waste) with enhanced penetration capability.
2. Timber Grab: Designed with elongated, toothed jaws to secure long-shaped materials (e.g., logs, pipes) and prevent slippage or rolling.
3. Dust-Proof Grab: Enclosed structure to minimize dust leakage, used in environmentally sensitive areas (e.g., grain, fly ash handling).
4. Underwater Grab: Waterproof and corrosion-resistant for dredging or underwater material recovery.
5. Waste Grab: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, specialized for waste treatment or scrap handling.
Specialized Types
Electromagnetic Grab: Combines electromagnetic plates with mechanical gripping, suitable for magnetic materials like metal scraps.


Characteristics of Grab Buckets
High Efficiency: Designed for rapid grabbing, lifting, and unloading of bulk materials, significantly improving operational productivity.
Adaptability: Customizable jaw configurations (e.g., multi-jaw, toothed, enclosed) to handle diverse materials like coal, scrap metal, logs, or fine powders.
Robust Structure: Built with durable materials (e.g., high-strength steel) to withstand heavy loads, abrasion, and harsh environments.
Flexible Drive Systems: Options include rope-driven (single/double rope), electric, or hydraulic mechanisms, catering to different power requirements and operational precision.
Safety & Environmental Control: Features like dust-proofing, corrosion resistance, or electromagnetic compatibility ensure safe and eco-friendly operations.
Applications of Grab Buckets
Ports & Terminals:
Loading/unloading bulk cargo (coal, ore, grain) from ships or trucks.
Handling containers or scrap metal with specialized grabs.
Mining & Quarrying:
Excavating and transporting heavy materials like rocks, minerals, or aggregates using hydraulic grabs.
Construction & Demolition:
Moving debris, sand, or gravel; lifting steel beams or pipes with timber grabs.
Waste Management & Recycling:
Sorting and transferring industrial waste, municipal garbage, or recyclables with lightweight, corrosion-resistant grabs.
Specialized Environments:
Underwater: Dredging rivers or salvaging submerged materials with waterproof grabs.
High-Dust Areas: Transporting cement, fly ash, or chemicals using sealed dust-proof grabs.
Components of a Grab Bucket and Their Functions
The structural design of a Grab Bucket directly impacts its grabbing efficiency and durability. It typically consists of the following core components:
1. Jaws (Clamshells)
Composition:
Two or more curved plates made of high-strength steel or alloy, with optional wear-resistant teeth or blades on the edges.
Functions:
Directly contact and grip materials, forming an enclosed space through closing motions to contain the load.
Teeth or blade designs enhance penetration into hard or loose materials (e.g., ore, scrap metal).
2. Drive System
Composition:
Hydraulic Drive: Hydraulic cylinders, pipelines, and control systems.
Rope-Driven System: Steel ropes, pulley blocks, and opening/closing mechanisms (dual-rope or single-rope systems).
Electric Drive: Built-in motors, gearboxes, and transmission devices.
Functions:
Provide power to open/close the jaws (grabbing and unloading).
Adapt to different operational requirements based on grab type (hydraulic/electric/rope-driven).
3. Support and Connection Structure
Composition:
Upper Crossbeam: Main load-bearing frame connecting to the crane hook.
Lower Crossbeam: Structural support for fixing the jaws and transmitting closing forces.
Hinge Pins: Rotational joints linking the jaws to the crossbeams.
Functions:
Bear the total load of the grab and materials, ensuring structural stability.
Enable flexible jaw movement via hinges, optimizing grabbing angles.
4. Pulley Block and Rope Guidance System
Composition: Steel ropes, pulleys, guide wheels, and balance beams.
Functions:
In rope-driven grabs, convert the crane winch's pulling force into jaw movement via pulley blocks.
Balance force distribution and reduce rope wear.
5. Sealing and Protection Devices
Composition:
Dust Covers: Sealed structures covering jaw seams (used in dust-proof grabs).
Waterproof Coatings: Corrosion-resistant materials (for underwater grabs).
Wear-Resistant Liners: High-hardness protective layers on the inner walls of jaws.
Functions:
Prevent material leakage or dust dispersion (e.g., grains, fly ash).
Extend grab lifespan by minimizing damage in corrosive or underwater environments.
6. Control System (Optional)
Composition: Sensors, solenoid valves (hydraulic grabs), remote control devices, or automation modules.
Functions:
Precisely control jaw opening/closing range and gripping force.
Enable remote operation or integration with crane systems (e.g., automated terminals).

 Port Cranes
Port Cranes  Overhead Cranes
Overhead Cranes  Gantry Cranes
Gantry Cranes  Rubber-Tired Gantry Cranes
Rubber-Tired Gantry Cranes  Jib Cranes
Jib Cranes  Bridge Beam Launcher
Bridge Beam Launcher  Light-duty Cranes
Light-duty Cranes  Electric Hoists
Electric Hoists  Electric Winch
Electric Winch  Electric Flat Car
Electric Flat Car  Crane Accessories
Crane Accessories  Hydraulic Lifting Platform
Hydraulic Lifting Platform  General Manufacturing
General Manufacturing  Heavy Machinery Manufacturing
Heavy Machinery Manufacturing  Bulk Cargo Yard
Bulk Cargo Yard  Metallurgical Industry
Metallurgical Industry  Power Industry
Power Industry  Hydraulic Engineering
Hydraulic Engineering  Railway/Rail Transit
Railway/Rail Transit  Port Terminal
Port Terminal  Construction and Engineering
Construction and Engineering  Shipbuilding
Shipbuilding  Waste Recycling
Waste Recycling