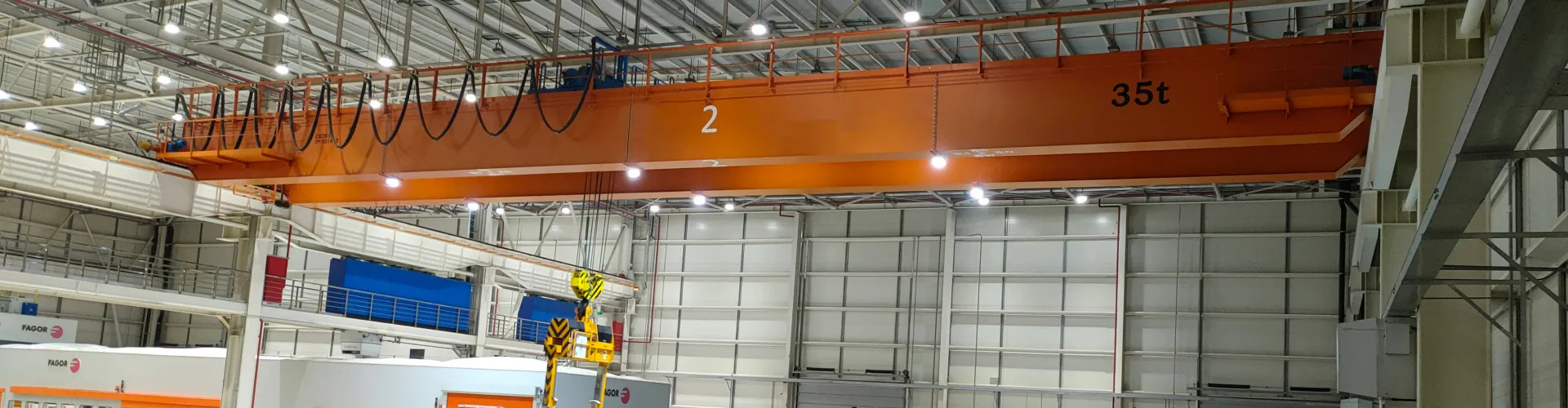
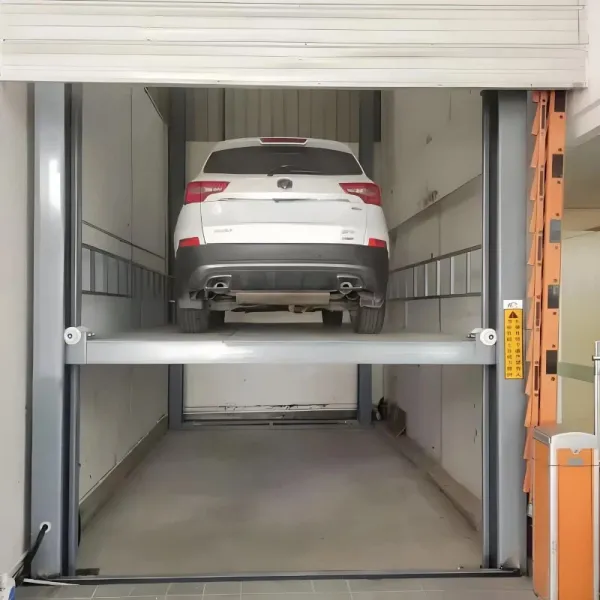
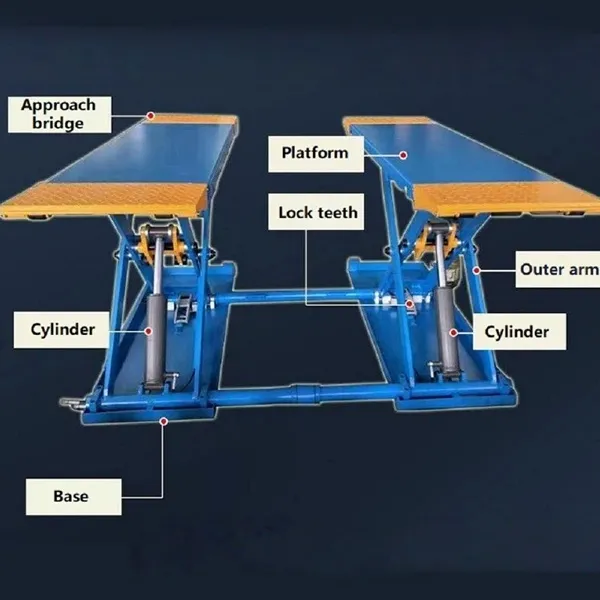
Vehicle lift is a device specially designed for lifting cars, usually installed in places such as stereo garages and underground garages. It is powered by a hydraulic system and can lift the car from the ground to a certain height for easy repair, maintenance or storage.
Common types of vehicle lifts include four-post, two-post, scissor, hydraulic, and pneumatic. The four-post type is supported by four pillars and driven by a bottom lifter. It has strong stability and is suitable for large vehicles; the two-post type has two pillars and a lifter, which takes up little space and is often used for light vehicle maintenance. The scissor type is based on the principle of scissors and operates through a hydraulic system. The hydraulic type can lift the vehicle to a higher place, while the pneumatic type is driven by air pressure. They each have their own characteristics and play an important role in different scenarios.
In addition to the above common types, there is also a rail-type car lift. This type of lift guides the car up and down through the rails. The operation process is smooth and orderly, just like a train running along the rails, providing precise guidance for the lifting of the vehicle. Rail-type car lifts are often used in places where there are specific requirements for space utilization and where vehicles need to be lifted and lowered accurately, such as special vehicle parking areas in some underground parking lots, allowing vehicles to reach designated locations safely and accurately.

|
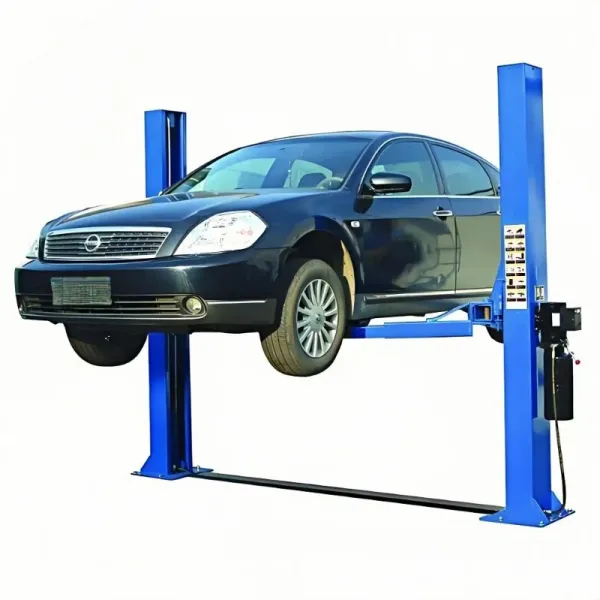
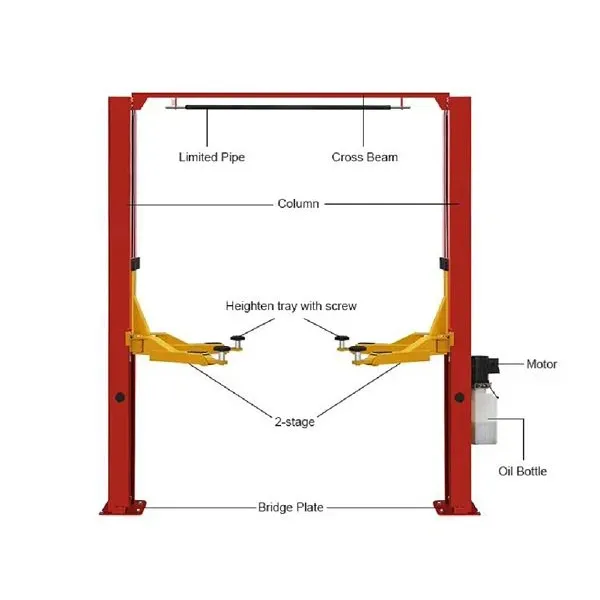
Two-Post Vehicle Lifts Consisting of two sturdy vertical columns, with each column housing a synchronized lifting system connected by wire ropes or chains. This system ensures the swing arms on both sides rise and descend at the same speed. The swing arms are equipped with adjustable pads to adapt to the lifting points of different vehicle models. Core Characteristics: As the entire underbody of the vehicle is completely suspended without any ground obstructions, maintenance personnel can access most areas of the chassis unobstructed, allowing for convenient movement and various repair tasks. By adjusting the swing arms, it can lift most passenger vehicles, from small cars to medium-sized SUVs. They typically require secure floor anchoring and have specific power requirements for the workshop. Application Scenario: Are the standard equipment in comprehensive repair shops, quick-lube/maintenance shops, and 4S stores. They are ideally suited for most underbody jobs like oil changes, brake pad replacement, chassis inspection, and exhaust system repairs. |
|
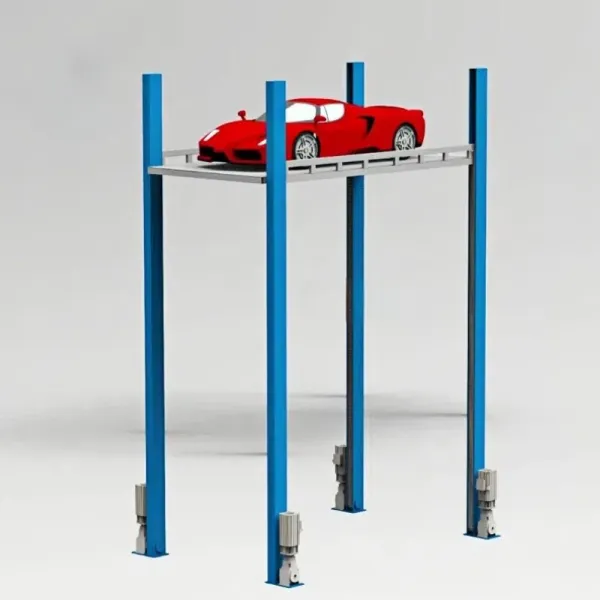
Four-Post Vehicle Lifts Comprising a robust rectangular base frame and four vertical posts, forming a complete lifting platform. Vehicles drive directly onto the runways of the platform, which is then raised synchronously via hydraulic or mechanical power. Core Characteristics: The four-point support structure is extremely stable, offering a load capacity far exceeding that of two-post lifts, generally above 4 tons. Heavy-duty models can lift trucks, buses, and even engineering machinery weighing tens of tons. Many four-post lifts are used in conjunction with a "secondary lifting jack," which can raise a single wheel after the main platform is elevated, used for tire changes or suspension testing. Vehicles can be driven directly onto them without precisely finding lifting points, making operation simple. Furthermore, the large support area on the underbody distributes pressure, reducing the risk of damage. Compared to two-post lifts, they require a larger installation space. Application Scenario: Due to their high load capacity, are widely used in truck repair stations, bus fleet maintenance centers, and situations requiring wheel alignment and comprehensive chassis inspections. Their platform stability also makes them suitable for long-term vehicle parking and display. |
|
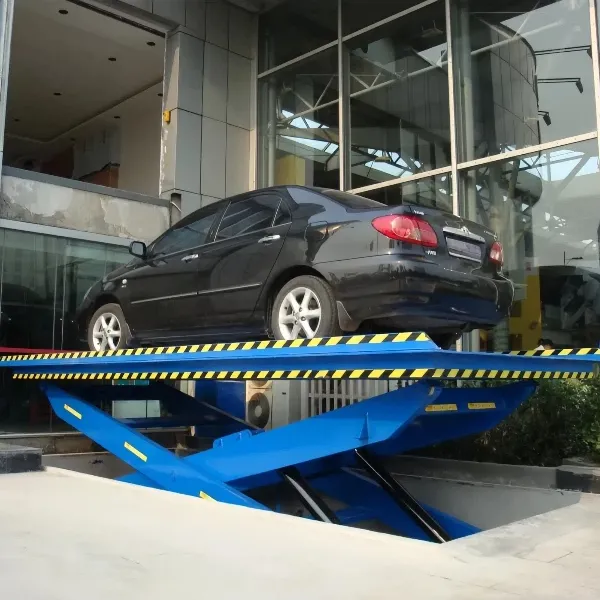
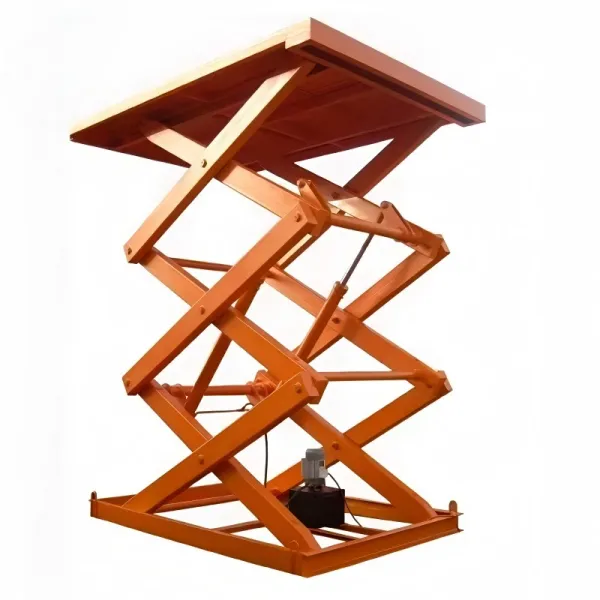
Scissor Vehicle Lifts Their core component is a set of cross-braced 'X'-shaped arms. Driven by hydraulic cylinders, these arms scissor open and closed to raise and lower the platform. They can be classified as "flush-mounted" (where the entire mechanism can be hidden below floor level) or "surface-mounted" (placed directly on the floor). Core Characteristics: When not in use, flush-mounted scissor lifts are level with the workshop floor, occupying no above-ground space. This keeps the workshop tidy, spacious, and facilitates vehicle movement and positioning. Due to their mechanical structure and synchronization system, the lifting process is very stable and precise, making them particularly suitable for tasks requiring high accuracy, such as wheel alignment. Similar to four-post lifts, vehicles are driven directly onto them, making operation straightforward. Application Scenario: Are the ideal choice for high-end automotive service centers, brand-specific dealerships, and shops specializing in wheel alignment and tire services. Their clean appearance and precise lifting effectively enhance the shop's professional image and work accuracy. |
-
 High-strength manganese steel scissor lift has a stable structure and large load-bearing capacity.
High-strength manganese steel scissor lift has a stable structure and large load-bearing capacity. -
 Precision grinding hydraulic cylinder
Precision grinding hydraulic cylinder -
 Emergency manual lowering valve and automatic relief valve in case of overload
Emergency manual lowering valve and automatic relief valve in case of overload -
 Homemade hydraulic system, low motor noise, long service life, 3-4 meters/minute. Lifting speed, lowering speed adjustable.
Homemade hydraulic system, low motor noise, long service life, 3-4 meters/minute. Lifting speed, lowering speed adjustable. -
 2-stage
2-stage -
 Arm-locking
Arm-locking -
 Chain
Chain -
 Control unit
Control unit

 Port Cranes
Port Cranes  Overhead Cranes
Overhead Cranes  Gantry Cranes
Gantry Cranes  Rubber-Tired Gantry Cranes
Rubber-Tired Gantry Cranes  Jib Cranes
Jib Cranes  Bridge Beam Launcher
Bridge Beam Launcher  Light-duty Cranes
Light-duty Cranes  Electric Hoists
Electric Hoists  Electric Winch
Electric Winch  Electric Flat Car
Electric Flat Car  Crane Accessories
Crane Accessories  Hydraulic Lifting Platform
Hydraulic Lifting Platform  General Manufacturing
General Manufacturing  Heavy Machinery Manufacturing
Heavy Machinery Manufacturing  Bulk Cargo Yard
Bulk Cargo Yard  Metallurgical Industry
Metallurgical Industry  Power Industry
Power Industry  Hydraulic Engineering
Hydraulic Engineering  Railway/Rail Transit
Railway/Rail Transit  Port Terminal
Port Terminal  Construction and Engineering
Construction and Engineering  Shipbuilding
Shipbuilding  Waste Recycling
Waste Recycling